Intermittent fasting has become a popular weight-loss strategy, offering potential health benefits beyond losing weight. This eating pattern alternates between fasting periods and eating periods, with well-known methods including the 5:2 Diet, 16/8 Method, and Eat-Stop-Eat. Intermittent fasting is praised for potential benefits beyond weight loss, such as improved metabolic health, better blood sugar regulation, and enhanced heart health. Gaspari Nutrition highlights that combining intermittent fasting with a healthy diet can optimize results.
Intermittent Fasting: At a Glance
- Intermittent fasting alternates between eating and fasting periods, offering benefits like weight loss, improved metabolic health, and better blood sugar regulation.
- Popular methods include the 5:2 Diet, the 16/8 Method, and Eat-Stop-Eat, each with different fasting and eating windows.
- Starting intermittent fasting requires gradual adjustment, staying hydrated, and avoiding common mistakes like fasting too long or overeating during eating windows.
What Is Intermittent Fasting?

Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that alternates between eating and fasting periods.
Research suggests that intermittent fasting can be an effective weight-loss strategy when paired with nutrient-dense foods during meals.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Here are some of the main benefits associated with intermittent fasting:
- Weight loss and improved body composition.
- Better blood sugar control.
- Reduced inflammation in the body.
- Enhanced heart health.
- Increased mental clarity and focus.
- Potential for a longer lifespan.
- Improved cellular repair processes.
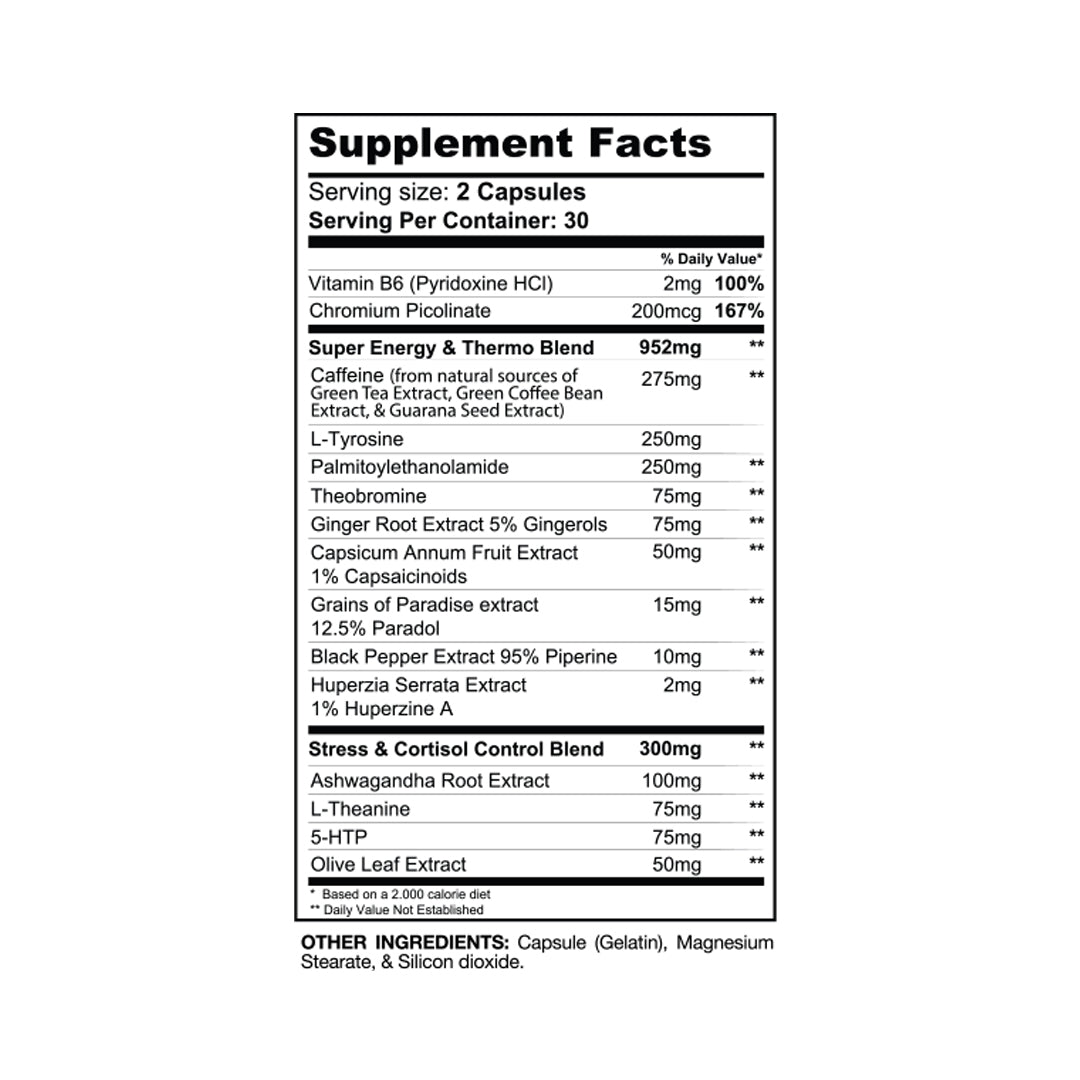
Gaspari Nutrition offers many supplements that can help you achieve your wellness goals. Check them out here:
Popular Intermittent Fasting Methods

The 5:2 Diet
The 5:2 Diet consists of eating normally for five days a week while limiting calorie intake to 500-600 calories on any two non-consecutive days. This approach allows for flexibility in choosing fasting days and can be easier to maintain long-term.
The 16/8 Method
The 16/8 Method, also known as time-restricted feeding, involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window daily. Typically, this means skipping breakfast and eating two meals between noon and 8 p.m.
Eat-Stop-Eat
Eat-Stop-Eat involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week. For example, fasting from dinner one day to dinner the next day. This method can be challenging for beginners but may offer significant benefits for those who can adapt to it.
Who Should Avoid Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Please consult with a physician before beginning.
The following groups should be cautious about or avoid intermittent fasting:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- People with a history of eating disorders.
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes.
- Those with low blood pressure.
- People taking certain medications that require food intake.
- Underweight individuals.
- Children and teenagers under 18.
- Elderly individuals with frailty or cognitive decline.
Tips for Starting Intermittent Fasting
Implementing these tips can help you transition smoothly into intermittent fasting and maximize its benefits:
- Start gradually: Begin with a 12-hour fast overnight, including sleep time. This gentle approach helps your body adjust before extending fasting periods.
- Stay hydrated: Drink water, unsweetened tea, or black coffee during fasting periods to curb hunger and maintain hydration.
- Plan nutrient-dense meals: Focus on consuming whole foods that are rich in protein, healthy fat, and some complex carbohydrates during eating windows to support your body's nutritional needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To maximize the benefits of intermittent fasting and support a smooth adaptation, steer clear of these common mistakes:
- Fasting Too Long: Extended fasts (24+ hours) can be counterproductive for beginners. They may lead to increased hunger, overeating during eating windows, or even slowing down metabolism. Start with shorter fasting periods and gradually increase them as your body adapts.
- Overeating During Eating Windows: Consuming excess calories during eating periods can negate the benefits of fasting. Avoid viewing eating windows as opportunities to indulge excessively.
- Neglecting Hydration: Proper hydration is crucial during fasting periods. Drink plenty of water, and consider calorie-free beverages like black coffee or herbal tea to help manage hunger.
- Ignoring Nutritional Balance: While fasting can aid weight loss, it's not a substitute for a healthy diet. Make sure your meals contain a good balance of proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
- Pushing Too Hard, Too Fast: Ease into intermittent fasting gradually. Jumping into extreme fasting schedules can lead to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty adhering to the plan.
FAQs
Can I Drink Water During Fasting Periods?
Yes, you can drink beverages with very few calories, such as water, plain sparkling water, and unsweetened black coffee and tea. These drinks can help hold off hunger without breaking your fast.
What Can I Eat During My Eating Window?
During your eating window, there are no strict restrictions, but focusing on high-quality foods is essential. A balanced diet rich in whole foods can enhance the benefits of intermittent fasting by stabilizing blood sugar levels, which will make your next fasting period easier.
How Long Does it Take to See Results?
People may start to notice changes within a few weeks, including weight loss and improved energy levels. However, significant changes, like more pronounced weight loss or metabolic benefits, might take a few months. Consistency is key to achieving and maintaining results.
Is Intermittent Fasting Safe for Everyone?
Intermittent fasting is safe for many but not for everyone. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals and those with medical conditions like kidney stones, disordered eating, or diabetes should consult their doctor before starting.












































































Share:
Creatine vs Creatinine: What's the Difference?
Understanding Glucose Metabolism: How Your Body Turns Sugar into Energy